Table Of Content
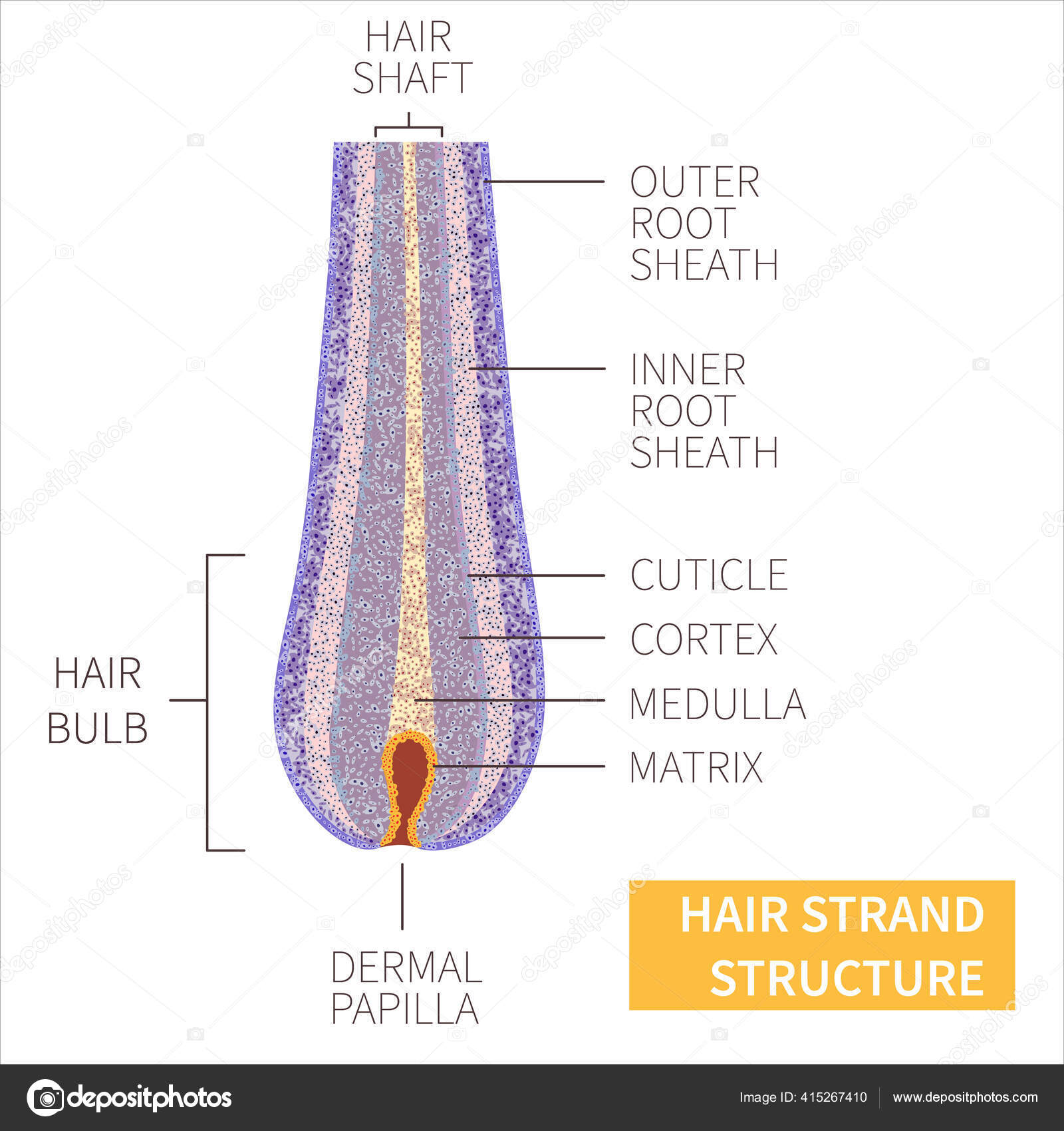
The hair shaft is the part of the hair not anchored to the follicle, and much of this is exposed at the skin’s surface. The rest of the hair, which is anchored in the follicle, lies below the surface of the skin and is referred to as the hair root. The hair root ends deep in the dermis at the hair bulb, and includes a layer of mitotically active basal cells called the hair matrix. The hair bulb surrounds the hair papilla, which is made of connective tissue and contains blood capillaries and nerve endings from the dermis (Figure 1). In the second stage of development, hair germ elongates into a cord of epithelial cells and forms the hair peg (stages 3 and 4). It is surrounded by mesenchymal cells that eventually transformed to the fibrous sheath.
The medulla of a hair under a microscope
The human hair is formed by divisions of cells at the base of the follicle. As the cells are pushed upward from the follicle’s base, they become keratinized (hardened) and undergo pigmentation. In addition, the hair labeled diagram shows a highly vascularized connective tissue layer that surrounds the outer root layer of the hair follicle. The microscopic figure of the hair follicle shows the basal lamina that separates the outer root layer from the connective tissue layer. This basal lamina is the glassy membrane of the hair follicle structure. The glassy membrane of the hair follicle structure is strongly eosinophilic.

The Hair Bulb
When the hair has separated completely from the papilla, the supply of blood is cut off in the final resting phase, which is also called the telogen phase. The hair is gradually pushed out of the skin and eventually falls out. The full strand of hair develops from this group of hardened hair cells. Because new hardened cells keep on attaching to the hair from below, it is gradually pushed up out of the skin. In this way, a single hair on your head grows at a rate of about 1 cm per month. Facial hair, and especially eyelashes, eyebrows and body hair grows at a slower pace.
Types of the cuticle of the hair shaft
Specialized hairs called vibrissae, or whiskers, serve as sensory organs for certain nocturnal animals. The specially modified hairs of the porcupine are called quills and serve defensive purposes. The cross-sectional shape of hair also determines the amount of shine that the hair has. Straighter hair is shinier because sebum from the sebaceous gland can easily travel down the hair. With curly hair, the sebum has trouble traveling down the hair, making it look more dry and dull.
First, let’s see the microscopic image of an animal’s hair and try to identify its following features. All the following microscopic features are well identified in the hair-labeled diagram. Similar to the skin, hair gets its color from the pigment melanin, produced by melanocytes in the hair papilla. Different hair color results from differences in the type of melanin, which is genetically determined. As a person ages, the melanin production decreases, and hair tends to lose its color and becomes gray and/or white. The cuticle is your hair’s protective layer, composed of overlapping cells — like fish scales or roof tiles, but facing downwards.
A Guide to Microlink Hair Extensions - Women's Health
A Guide to Microlink Hair Extensions.
Posted: Thu, 26 Oct 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Structure of hair shaft under a microscope
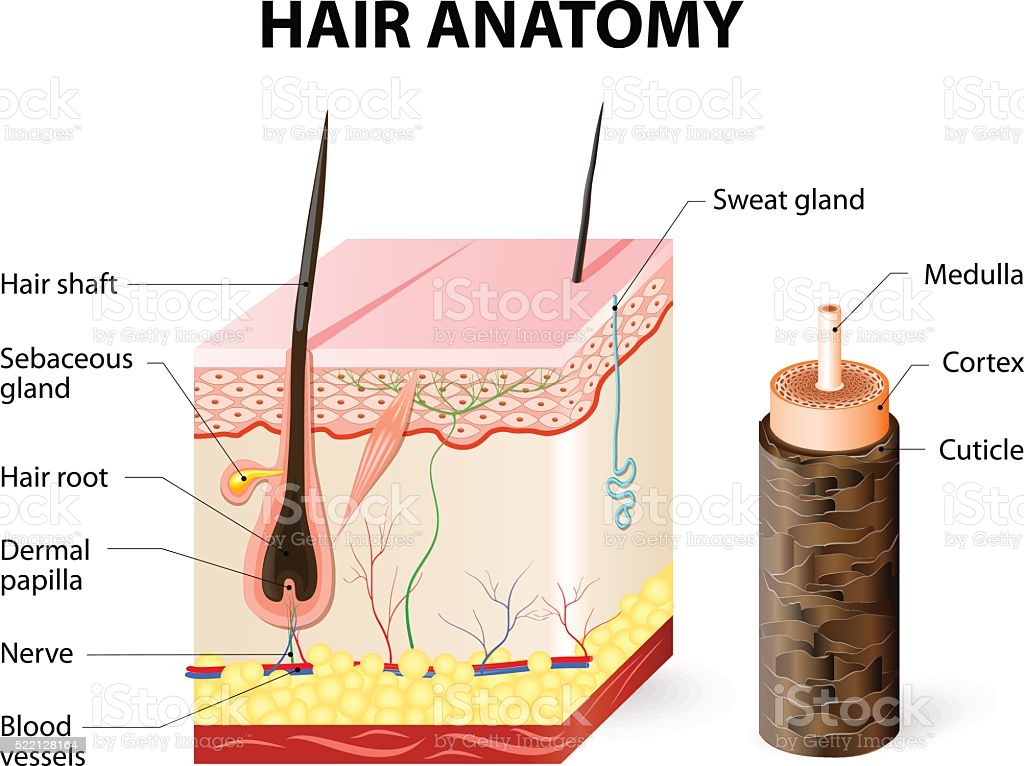
Hair growth begins with the production of keratinocytes by the basal cells of the hair bulb. As new cells are deposited at the hair bulb, the hair shaft is pushed through the follicle toward the surface. Keratinization is completed as the cells are pushed to the skin surface to form the shaft of hair that is externally visible. The external hair is completely dead and composed entirely of keratin. Furthermore, you can cut your hair or shave without damaging the hair structure because the cut is superficial. Most chemical hair removers also act superficially; however, electrolysis and yanking both attempt to destroy the hair bulb so hair cannot grow.
Hair and follicle morphology
But, the length and texture of the hair are different in the different regions of the animal or human body. This specialized immune environment of IP is required to prevent destructive immune reactions in critical regions. Other immune privileged sites include the anterior chamber of the eye, testis, brain and placenta. Hair follicle IP has a unique characteristic of recurring in a cyclic pattern. The hair follicle is a skin appendage located deep in the dermis of the skin. From the inside out, these are the medulla, cortex, and cuticle.
An Illustrated History of Donald Trump's Hair. Warning! Don't Read Before Lunch! - Vanity Fair
An Illustrated History of Donald Trump's Hair. Warning! Don't Read Before Lunch!.
Posted: Tue, 08 Sep 2015 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Microscopically, you will find minute air bubbles both in the medulla and the cortex of the hair shaft. Each hair of an animal consists of two parts – one visible on the body surface and another part anchored in the thickness of the skin. The visible part of the hair is known as the shaft, and the embedded part is the hair root.
In the great majority of cases, however, it is simply a matter of aging. The hair matrix is the epithelial layer involved in hair production. When the superficial basal cells divide, they produce daughter cells that are pushed toward the surface as part of the developing hair. The medulla contains relatively soft and flexible soft keratin. Matrix cells closer to the edge of the developing hair form the relatively hard cortex. The cortex contains hard keratin, which gives hair its stiffness.
In this chapter, the basic anatomy and the amazing and complicated biology of the hair follicle is reviewed. Enhanced knowledge on the normal dynamics of the hair provides understanding the basis of how the follicle behaves during a disease. However recent progress in our understanding of the biology and pathology of hair follicles should lead more effective therapies for hair disorders. Hair shaft moisture is actually in the medulla and is held in the central part of the hair shaft. The cuticle (the outer layer of the hair shaft), serves among other things to allow moisture to come in and out of the medulla. The cuticle protects the medulla from harmful environmental agents , sun, wind, pollution chemicals and other toxin.
So, the cells of the lower end of the hair root and hair bulbs possess the germinative matrix. So, let’s discuss these three different layers of the hair follicle with their microscopic features. I will show all these microscope figures of different animals’ hair in the labeled diagrams section.
No comments:
Post a Comment