Table Of Content
I hope you already got these specific characteristics of hairs from different animals and can identify them under a light microscope. So, when you find these characteristic features under a light microscope, you may easily tell them hairs. Again, you may identify the hair based on specific identifying features in different animals. The medulla of the rabbit hair shaft is a multiserial ladder and shows a ribbon-like appearance.
Hair Loss Myths Debunked
When taking history in a patient with hair loss, it is imperative to determine what the patient is experiencing. Hair loss can refer to increased daily hair loss, which a clinician will elicit by asking if the patient notices more hair on his or her pillow or more hair in the shower after bathing. Teasing out this distinction is necessary to determine the correct diagnosis. Compare secreation of Sebum fram sebaceous gland vs shea butter and their similarities.
Structure and Function
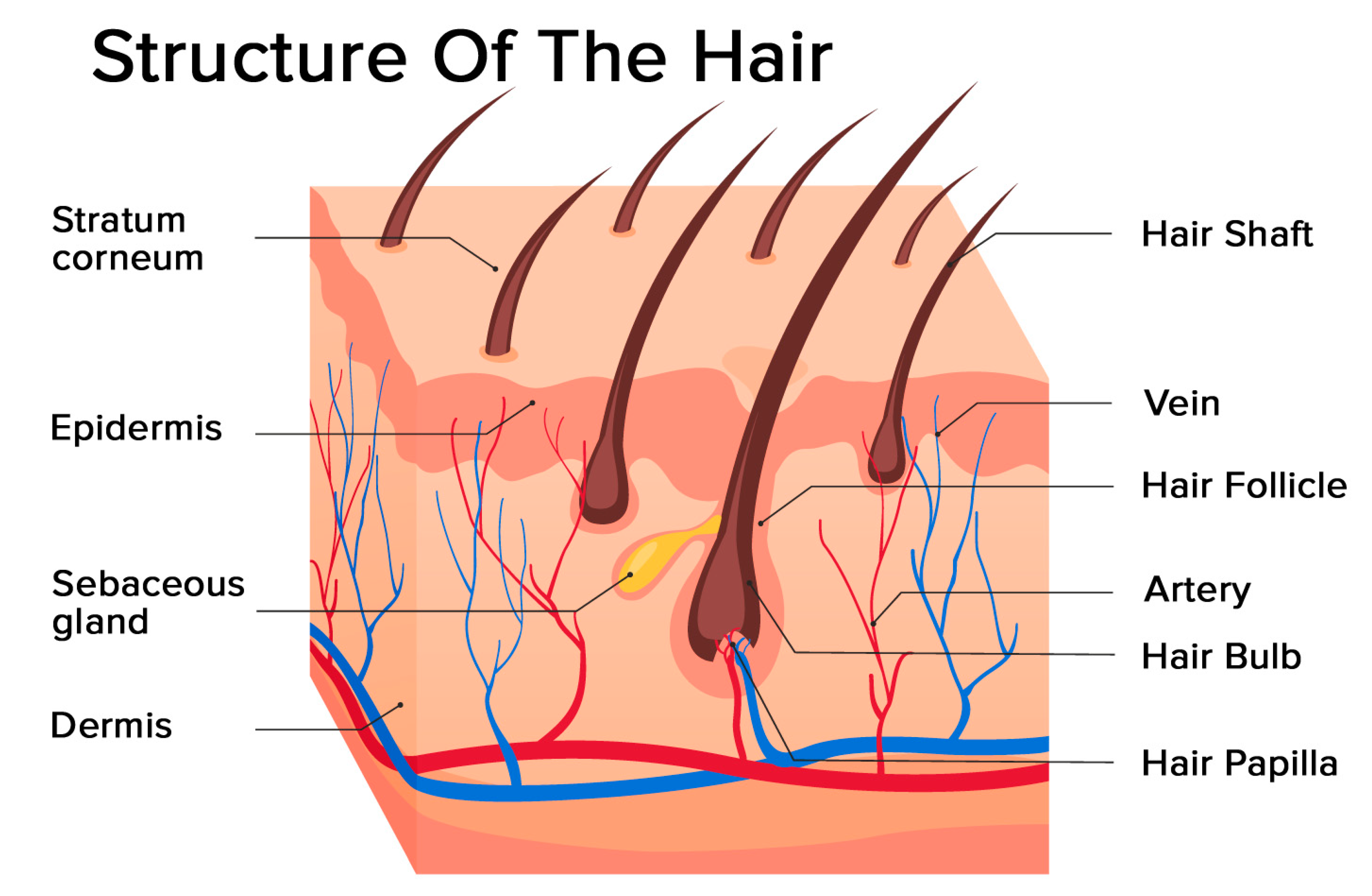
During the first few months of infancy there grow fine, short, unpigmented hairs called down hair, or vellus. Vellus covers every part of the body except the palms of the hands, the soles of the feet, undersurfaces of the fingers and toes, and a few other places. The hairs of the scalp, eyebrows, and eyelashes are of separate types from these others and develop fairly early in life. On the scalp, where hair is usually densest and longest, the average total number of hairs is between 100,000 and 150,000. Human hair grows at a rate of about 0.5 inch (13 mm) per month. The hair follicle sits underneath the skin’s surface and extends down into the dermis layer of your skin.
Hair Follicles
The bulge producesstem cells which regenerate the follicle during the next hair growth cycle. This produces an oily substance calledsebum from a duct which opens up into the hair follicle about halfway downfrom the skin surface. Three different types of hair cell then form(see hair shaft structure diagram below). By the time these cells are a third ofthe way up the follicle, they have died and fully hardened (keratinized). The dermis then grows upwards into the base of thefollicle to form the dermal papilla.
How to Use Hot Rollers to Create 4 Different Hairstyles, Including a Blowout and Beach Waves - Martha Stewart
How to Use Hot Rollers to Create 4 Different Hairstyles, Including a Blowout and Beach Waves.
Posted: Thu, 29 Sep 2022 07:00:00 GMT [source]
The perifollicular sheath collapses and vitreous membrane thickens. Eventually, the lower hair follicle becomes reduced to an epithelial strand, bringing the dermal papilla into close proximity of the bulge [36]. The epithelial strand begins to elongate and finally reaches to just below the insertion of pilar muscle. The column eventually reduces to a nipple and forms secondary hair germ below the club. The club hair itself is formed from cortical and cuticle cells only, and it is characterized by a lack of pigmentation [2, 37]. The presence of hairless gene mutation contributes to the failure of dermal papilla migration toward the bulge area in catagen phase [3].
You will find different secretory cells in the structure of the sebaceous gland of an animal’s skin. So, let’s know the specific identifying features of a hair under a light microscope. Here, I will enlist some important identifying features of hair and hair follicles for transverse and cross-sectioned samples. There is less interest for the mechanism of the hair shedding but from the patient’s perspective it is probably the most important part of the hair growth. It is not unusual for human telogen hairs to be retained from more than one follicular cycle and this suggests that anagen and exogen phases are independent.
What microscope can see hair?
Hair is extremely sensitive to air movement or other disturbances in the environment, much more so than the skin surface. This feature is also useful for the detection of the presence of insects or other potentially damaging substances on the skin surface. This is visible in humans as goose bumps and even more obvious in animals, such as when a frightened cat raises its fur. Of course, this is much more obvious in organisms with a heavier coat than most humans, such as dogs and cats. Hair shaft synthesis and pigmentation only take place in anagen [11]. The degree of axial symmetry within the hair bulb determines the curvature of the final hair structure [35].
Two neural networks innervate hair and hair follicles, and both contain sensory nerve fibers and autonomic nerve fibers. One of the neural networks is made up of sensory C fibers and sympathetic fibers and surrounds the neck of the hair follicle. The other is made up of longitudinal A-delta fibers and circular C fibers and encircle the midsection of the hair follicle, between the isthmus and the sebaceous gland. Nearby nerves also innervate the proximal arrector pili muscles. Analysis of certified premium shea butter can replace sebum to accomplish moisturizing and to fill the gaps between cuticle cells and to keep hair shiny and flexible. Immediate help can be achieved through correct brushing to distribute natural Premium Grade shea butter,(important to note , see similarities between Sebum and Shea chemical makeup).
Hairs of other different animals
Lanugo, vellus and terminal hairs follow the same basic architectural principles. The first “coat” that is formed is fine, long, variably pigmented lanugo hair, which is shed in an anterior to posterior wave during last trimester of gestation. A second coat of fine, shorter, unpigmented lanugo hair then grows in all areas except the scalp and is shed 3–4 months after birth. After these first two cycles, hair starts to grow in an asynchronous “mosaic” pattern rather than in waves [2]. In utero, type and distribution of each hair follicle over the entire body are determined.
The keratin that makes up the major part of the hair is formed by amino acids molecules sourced from the food we eat. This protein is also found in our fingernails, toenails, and skin according to the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD). The shaft is the visible part of the hair that sticks out of the skin. The hair root is in the skin and extends down to the deeper layers of the skin.
You may find the fragmented, segmented, or continuous medulla in the hair. Spinous or petal-like scales of the cuticles are more or less triangular-shaped. These scales frequently protrude from the hair shaft of the animals. On the other hand, human hair contains fragmented, interrupted, or continuous medulla in its shaft. Again, there is some significant difference in the scale patterns of the cuticles of human and animal hairs. I think these identifying features of the hair shaft and follicle might help you identify the hair at your laboratory with the help of a light microscope.
Our team is growing all the time, so we’re always on the lookout for smart people who want to help us reshape the world of scientific publishing. Hairs first appear after about three months of embryonic development. These hairs, collectively known as lanugo, are extremely fine and unpigmented. Sixteen amino acids form keratin, with cysteine having the highest concentration.
No comments:
Post a Comment